I’ve gotten a lot of questions in and out of the office recently about E. coli and the current state of the open water swim venue in Paris. And so I thought it would be helpful to give a quick overview of what’s going on.
First of all, what is it? Escherichia coli (E. coli) in medical terms is a rod shaped gram-negative bacteria. It got its name Escherichia, from the German pediatrician Theodor Escherich, who discovered the bacteria in 1885. Its second name, coli, means “from the colon”, which is the organism’s natural habitat. 

Anyone who has been through medical school likely learned about E. coli by reading the book “Clinical Microbiology Made Ridiculously Simple,” and they were shown a cartoon image here of a baguette shaped bacteria with tails. They are what are known as “enteric” bacteria, which is just another way of saying that E. coli normally live in the intestines of healthy people.
Most E. coli are harmless and are part of a healthy intestinal tract. These E. coli help digest food, produce vitamins, and protect us from harmful germs. They help us break down food for absorption, and importantly, they are normally excreted in our waste. But some E. coli can make people sick, including about six kinds that cause diarrhea.
Exposure to these kinds of “pathogenic” E. coli can cause issues through different mechanisms. Some attach to the outside of the intestinal cells and produce a toxin that damages surrounding cells, leading to diarrhea. Others invade intestinal lining cells and injure them directly, causing… diarrhea. Diarrhea is harmful because it leads to a loss of significant amounts of fluid from the body as well as needed minerals that can lead to an imbalance.
And this is where the unique history of Paris plays a role. Every time I’ve been to Paris I make time to stop by the Musée des Egouts de Paris, which is The Paris Museum of Sewers (https://musee-egouts.paris.

But if walking through the sewers of Paris is not on your bucket list, I can sum up the problem for you. Due to the age of the city of Paris, and the evolution of the waste management system through the 1800’s, there are periods of time when heavy rainfall will inundate the unique combined sewer and rainwater system and cause an overflow in the Seine. And with it will come an increase in the levels of E. coli in the river. The tests they conduct are not able to discern the difference between good and bad E. coli. So the assumption has to be that the bad E. coli exist.
Normally, this wouldn’t be much of an issue. Because normally, there wouldn’t be an Olympic triathlon or open water swim event with the entire world watching. 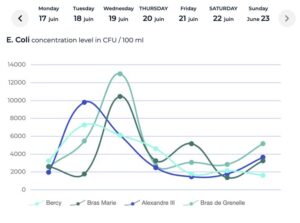

The good news is, we are still a month away from the Olympics. According to European standards and the World Triathlon Federation, the safe limit for E. coli is 900 colony-forming units per 100 milliliters. And the levels vacillate significantly over days, as seen in the chart below. Couple this normal variation with the likelihood of July bringing more sun, less rainfall, and warmer weather, there is a high probability that the E. coli levels will be down to acceptable levels in the coming weeks. As well, there is the option to delay the start of the open water swim events if trends show that an acceptable level would be attainable, according to Paris 2024 president Tony Estanguet.
While we should not be afraid of most E. coli, these safety limits exist for a reason. And there are still several weeks for the issue to correct itself. Time will tell how this will play out.